- Home
- AGRI-PV Module
AGRI-SOLAR MODULE
ZOEAST PV Agri-Pv modules generate clean energy while presering space for farming or livestock. this is invnovative solution maximizes both agricultural and green energy income, optimizing the use of every acre.
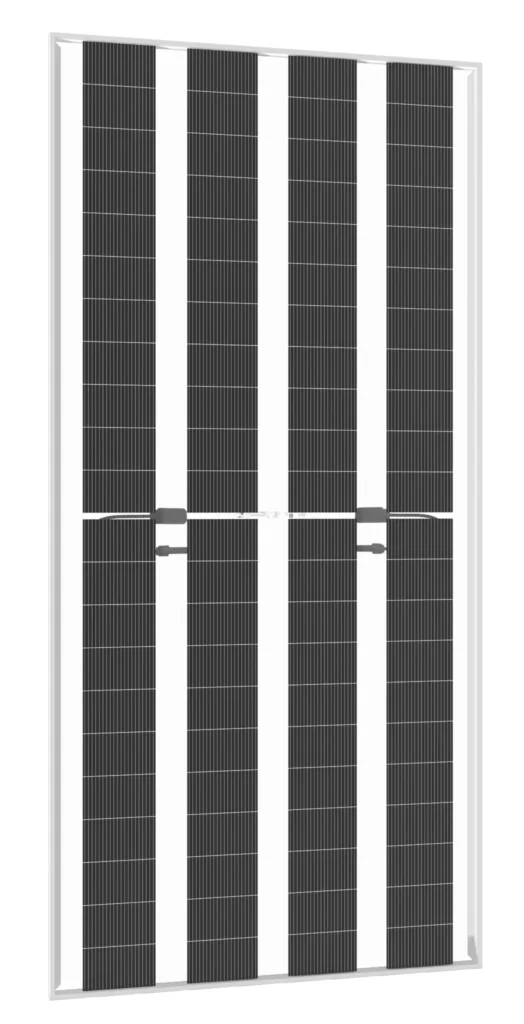
400-410W N TYPE BIFACIAL MODULE WITH DUAL GLASS
Solar Cells Type: N- type Mono-crystalline
No. of cells: 88(4x22)PCS
Size: 2382x1134x30mmmm
Weight: 32 kg.
Packing Detail
: 36 pcs/pallets,20pallets/cnt, 720pcs/ 40'HQ
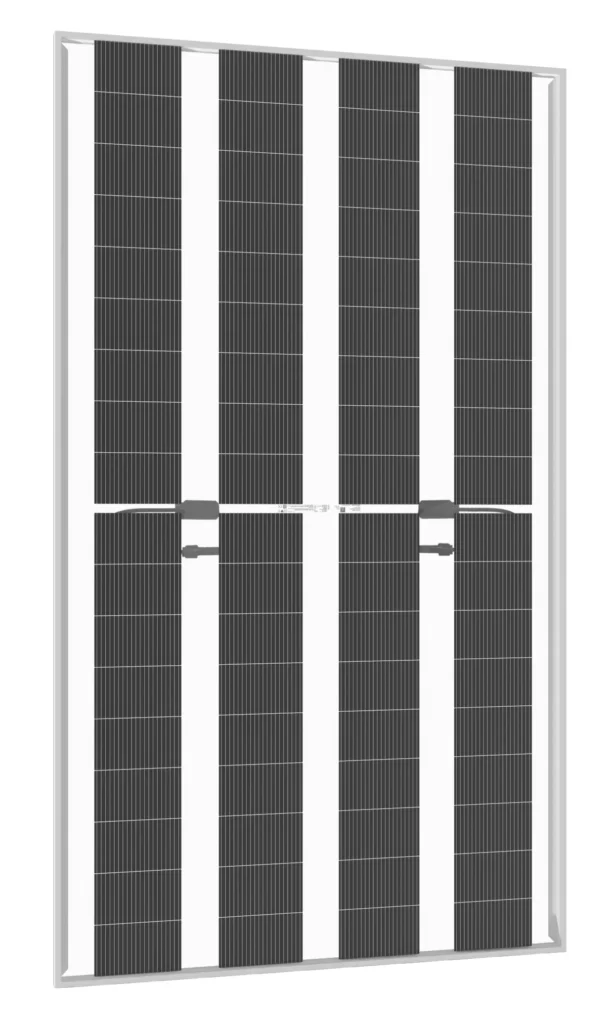
325-335W N TYPE BIFACIAL MODULE WITH DUAL GLASS
Solar Cells Type: N- type Mono-crystalline
No. of cells: 72(4x18)PCS
Size: 1960x1134x30mmmm
Weight: 26.9 kg.
Packing Detail
: 36 pcs/pallets, 24pallets/cnt, 864pcs/ 40'HQ
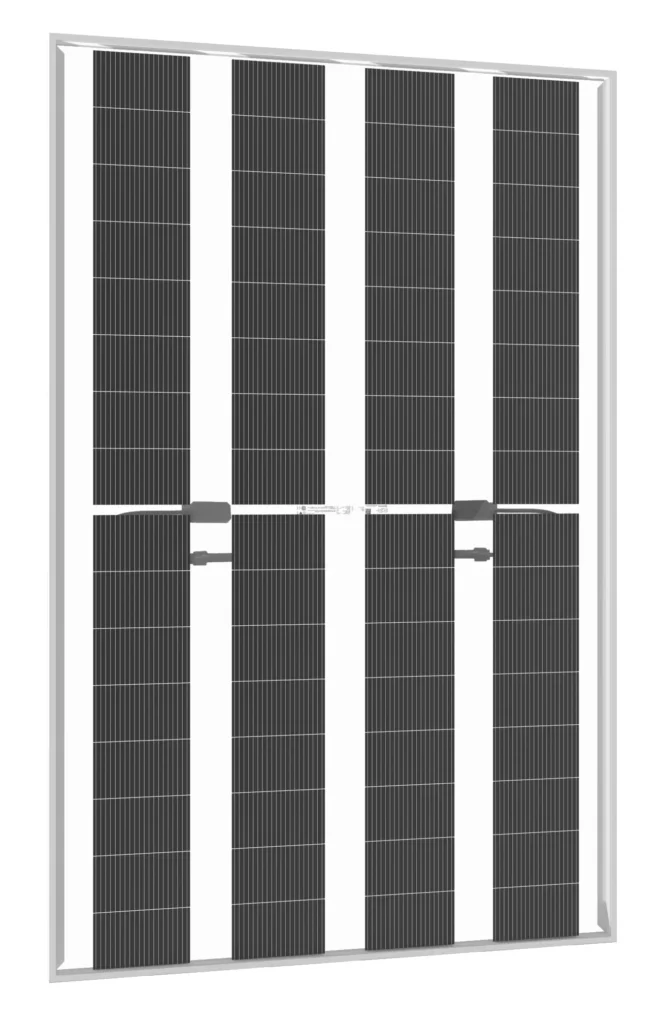
285-295W N TYPE BIFACIAL MODULE WITH DUAL GLASS
Solar Cells Type: N- type Mono-crystalline
No. of cells: 64(4x16)PCS
Size: 1762x1134x30mmmm
Weight: 21.5 kg.
Packing Detail
: 36 pcs/pallets, 26pallets/cnt, 936pcs/ 40'HQ
REQUEST A QUOTE FOR MORE DETAILS
All You Need To Know About Solar Panel!
1. What Are Solar Panels?
Solar panels are devices that convert sunlight into electricity. They are composed of solar cells made primarily of silicon, which use the photovoltaic (PV) effect to generate direct current (DC) electricity.
2. Types of Solar Panels
1. Monocrystalline Panels
– Made from a single crystal of silicon.– High efficiency (20–22%).
– Long lifespan and excellent performance in low light.
2. Polycrystalline Panels
– Made from multiple silicon crystals.– Moderate efficiency (15–17%).
– More affordable but slightly less efficient than monocrystalline.
3. Thin-Film Panels
– Made by depositing thin layers of PV materials (like cadmium telluride or amorphous silicon).– Flexible and lightweight but lower efficiency (10–12%).
4. Bifacial Panels
– Generate electricity on both sides of the panel.– Ideal for maximizing energy output in reflective environments.
3. How Solar Panels Work?
- Absorption of Sunlight: Solar cells absorb sunlight, exciting electrons in the silicon layers.
- Electric Current Creation: The movement of these electrons generates an electric current.
- Conversion to Usable Power: The electricity generated is DC, which is converted to alternating current (AC) using an inverter, suitable for household or commercial use.
4. Efficiency Factors
- Sunlight Intensity: Direct sunlight increases efficiency.
- Panel Orientation and Tilt: Facing true south (in the Northern Hemisphere) or true north (in the Southern Hemisphere) at the correct tilt angle maximizes energy capture.
- Temperature: High temperatures can decrease efficiency.
- Shading: Partial shading can significantly reduce output.
5. Applications
- Residential Rooftops: Powering homes, reducing electricity bills.
- Commercial Installations: Large-scale systems for factories, offices, and warehouses.
- Utility-Scale Solar Farms: Large fields of solar panels feeding electricity into the grid.
- Off-Grid Systems: Powering remote areas, RVs, boats, and emergency backups.
6. Key Components of a Solar System
- Solar Panels: Capture sunlight.
- Inverter: Converts DC to AC.
- Battery Storage (Optional): Stores excess energy for later use.
- Mounting Systems: Secure the panels to roofs or ground.
- Monitoring System: Tracks energy production and system health.
7. Benefits of Solar Panels
- Environmental: Reduces greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels.
- Economic: Lowers electricity bills and qualifies for tax incentives and rebates.
- Renewable Energy Source: Infinite and sustainable energy from the sun.
- Low Maintenance: Require minimal upkeep with periodic cleaning and inspections.
8. Challenges
- Initial Cost: High upfront costs for installation.
- Weather Dependency: Reduced efficiency during cloudy or rainy days.
- Space Requirements: Large installations need significant space.
- Recycling and Disposal: Managing end-of-life solar panels is a growing concern.
9. Innovations in Solar Technology
- Perovskite Solar Cells: Potential for cheaper and more efficient solar panels.
- Solar Shingles:Integrated roofing materials with built-in solar cells.
- Floating Solar Farms: Panels installed on water bodies to save space.
- Transparent Solar Panels: For windows and building facades.
10. Maintenance Tips
- Clean Panels Regularly: Remove dust, leaves, and debris.
- Check for Damage: Inspect for cracks or wear.
- Monitor Performance: Use monitoring apps to track efficiency.
- Professional Servicing: Annual inspections by professionals ensure optimal operation.